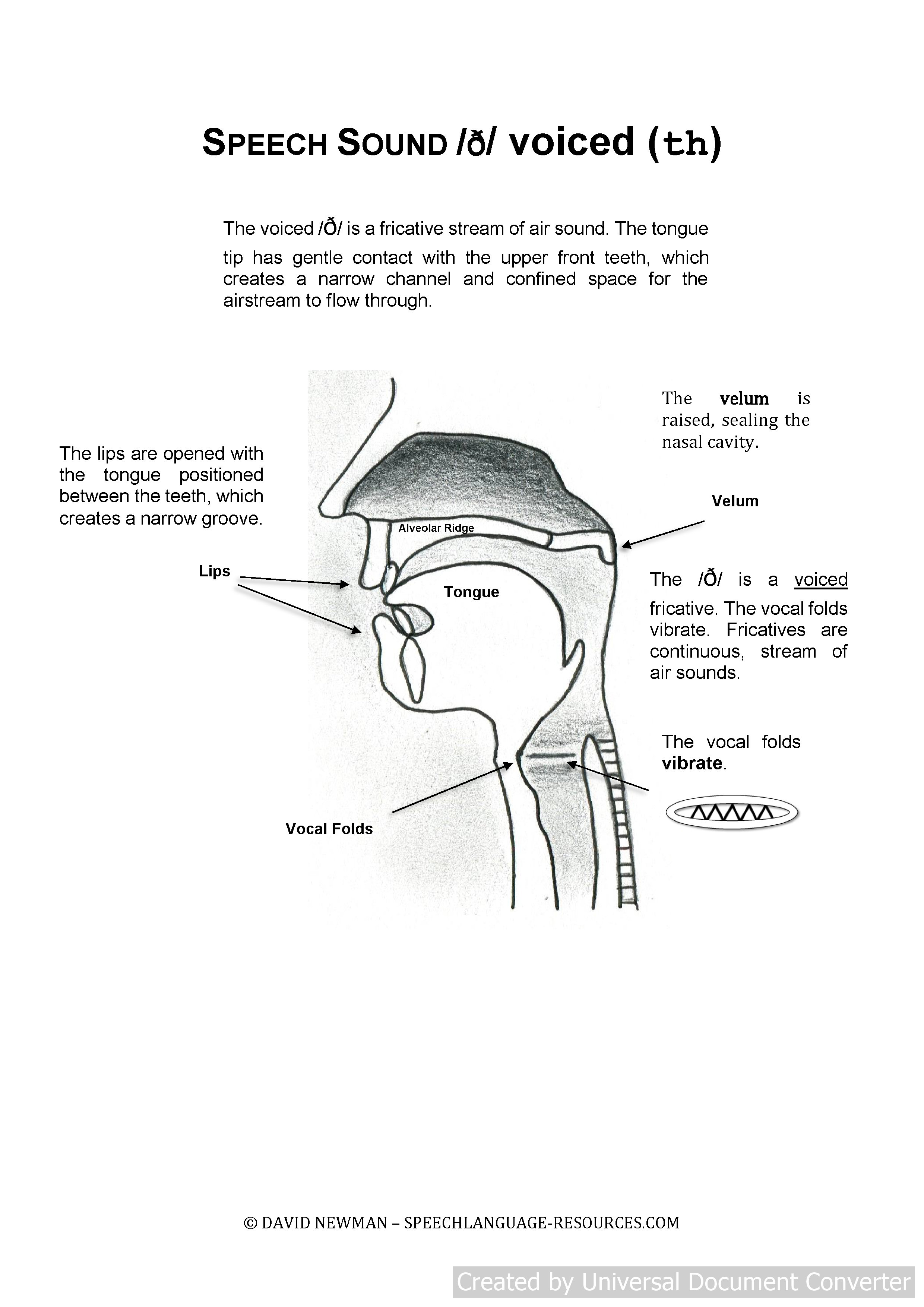
Speech Therapy Voiced th

Speech Therapy Voiced th: The voiced /ð/ is a fricative stream of air sound. The tongue tip has gentle contact with the upper front teeth which creates a narrow channel and con-fined space for the air-stream to flow through.
The compression of this narrow space creates a friction as the voiced air-stream flows through the restricted area. The jaw is lowered marginally to provide for the correct tongue positioning.
Speech Therapy Voiced th - Sound Errors
A common sound substitution for the /ð/ is the voiced stop /d/. So this becomes dis. The /ð/ sound is a later developing sound. Many children with typically developing speech and language don’t produce a correct /ð/ sound until 7-8 years of age and so should not be considered a sound error for children under 5-6 years of age.
Speech Sound Structures - /ð/ Sound
Click on image to download file
Speech Therapy Voiced th - Sound Stimulation
Demonstrate the characteristics of correct /ð/ production to your child.
- Demonstrate to your child what a typical /ð/ looks and sounds like by moving your tongue to allow the tip to poke between your teeth.
- Tell the child to copy your model and to note that the jaw is slightly opened and forward to accommodate the tongue position.
- Instruct your child to allow the air-stream to flow through the narrow space between the raised tongue and the upper teeth.
/ð/ Sound stimulation
Work through the following procedures with your child.
- The /ð/ sound is made by slightly lowering the jaw and contacting the upper teeth with the tongue.
- The contact between tongue and teeth creates a constriction through which the air-stream is directed.
- The tongue should be flat on /ð/ production. The /ð/ sound is a fricative stream of air sound and is voiced.
- The vocal folds vibrate.
Speech Therapy Voiced th - Sculpting from other Speech Sounds
Many speech sounds can be sculpted using other speech sounds as a starting point. This involves altering or adjusting speech sounds so that they approach the target sound in nature. This works by the clinician modeling a sound that the child is able to produce. The clinician then makes slight, progressive adjustments to the sound until the target sound is generated.
Sound sculpting from the /d/ sound
Instruct your child to initially hold tongue position for the /d/ sound. The child then slowly and progressively moves the tongue forward under the top teeth while maintaining the air-stream.
Sound sculpting from the /v/ sound
Instruct your child to produce the /v/ sound while being conscious where the tongue is positioned during /v/ production (it should be just behind the teeth not touching any structures). The child then slowly and progressively moves the tongue forward to essentially rupture the /v/ sound. The tongue should be poking through the front teeth, which redirects the air-stream and produces a clear voiced /ð/ sound.
Updated 07/08/2020